A laser welding machine is used for precise welding needs over various metallic materials like aluminum, copper, stainless steel, and similar others. However, talking about the very reflective material like aluminum, it is little tough to weld, due to its certain oxidation and porosity problems. So, the welding quality needs to be very accurate and durable, to complete the high-quality welding.
Welding Machine

- 1kw welding machine
- 1.5kw welding machine
- 2kw welding machine
- Call or WhatsApp: 9804718718
- Starting price-TBD+GST
Properties of aluminum
Aluminum is a highly demanding product in multi-industrial applications. And it has a major uses in the automobile industry, utensil-making and kitchenware products, the aviation industry, and many others. So, first of all, we will be discussing its physical, chemical, and mechanical properties, so that we can easily identify its welding preferences.
Physical properties
| Ductility | High ductility. It can be beaten very thin. |
| Malleability | High malleability. |
| Thermal Expansion | thermal expansion coefficient of 23.2 |
| Corrosion | corrosive resistant due to a self-protecting oxide layer |
| Conductivity | Good electrical and thermal conductor. |
Chemical Properties
| Occurrence | compound, bauxite ore |
| Oxidation | aluminum oxide in moist air(reaction with oxygen ) |
| Reactivity with water | reacts with hot water |
| Reactivity with acid/alkalis | Reactive over acid/ sodium hydroxide |
| Alloy formation | iron, copper, manganese, silicon, magnesium, and zinc |
Mechanical Properties
| Tensile strength | 13,000 Psi |
| Fatigue strength | 5000 Psi |
| Shear Strength | 9000 Psi |
| Elongation at break | 15-28% |
| Elasticity in tension | Young’s modulus of 10000 ksi |
How challenging is Welding of Aluminum?
Due to some unique properties of aluminum, the laser welding process needs little affords. Here are some of the issues you may encounter while doing welding works over aluminum surfaces.
- Porosity problems
The aluminum welded surfaces face small porosity issues, due to mainly two reasons. Firstly, due to the dissolution of hydrogen (metal bath). Secondly, the aluminum surface shrinkages after its solidification. The aluminum welding once comes in contact with the environment’s effect i.e. hydrogen, temperature, humidity, wind speed, etc. It starts creating small pores over its surfaces, which starts metal degradation after some time. So, to avoid porosity, check the the level of gas flow and leaks with surface cleaning.

2. Cracks over Metal surfaces(low temperatures)
Due to the low melting (1,218 °F / 659 °C), its surfaces may crack, wrap and even break during the welding process. So, it would be an ultimate loss for further applications. So, it has to be weld is perfect using GMAW process. In this process, in between the base metal and a consumable electrode, pass the filler metal using an arc.

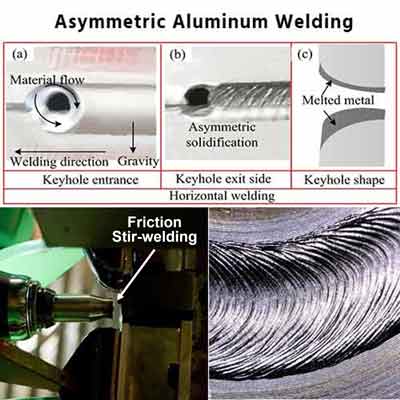
3. Asymmetric Parts
Aluminum has asymmetrical and tensile strength mechanical properties, due to this requires friction stir welded joint. Below is the picture for the better understanding.
4. Material Discoloration
During the aluminum surfaces welding, magnesium oxides can lead to discoloration. So, a welder needs to refill the appropriate filler material to avoid this issue. And, place the welding gun appropriately using the correct angle.

5. Hydrocarbon Contamination
Any kind of oil spillage, greasing, and any other contamination should be removed from the aluminum surfaces before the welding operations. As, it is the main reason for the aluminum oxides and hydrocarbon contamination, Further, it resists the welding quality and produces bad welds.

How to weld aluminum?
Aluminum is sensitive to environmental factors like, temperature influences, solvents, water, air etc. So, it needs very clean welding process, where you need to clean the surfaces. Here are some of the best methods to apply before initializing the welding operations.
- Clean the welding surfaces: Remove any spitted oil, greases, water vapors using an alkaline solvent to entirely clean the aluminum surfaces and avoid further oxidation.
- Remove dirts: To prevent the surfaces from the integration of dirt or grit from the contaminated joints, cover the surfaces before the welding.
- Set the temperature: Maintain the surface dryness at the moderate room temperature and clean properly to remove further contamination of the welding areas.
- Set up and Fix the machinery: Prepare all the machines equipment like welding machine, chiller, wire feeder, welding gun(nozzel, lens), argon cylinder etc.
- Wear the protective items: Always use the protective goggles, gloves and helmets to avoids any accidents during the welding operations.
- Carry on welding-operations: Proceed with the welding and join the material surfaces using the filler and welding gun and finally solidify it to make a final welding.
Further, you can easily handle the welding over the aluminum surfaces and it will also prevent bad welds and oxidation, contamination and porosity issues of aluminum weldings.
Best method of welding aluminum
The technically advanced welding machines helps in aluminum surfaces welding by many ways. And, this helps in improved quality, and deformity free welding. So, here we will be discussing on some of the famous welding techniques at industrial level:
1. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)/ TIG
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), also better abbreviated as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding. This technique uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode and creates an electric arc for joining the aluminum sheets.
In GTAW/TIG welding, a welder uses a torch for housing a tungsten electrode. It mainly uses the flow of an inert gas, typically argon, to protect the weld area from atmospheric contamination. The tungsten electrode, which has a high melting point, remains unchanged during the welding process.

The heat generated by the electric arc melts the base metals, and filler metal can be added manually, if required, to form a weld pool. The molten pool solidifies to create a strong and precise weld joint. The inert gas shield prevents oxidation and contamination of the weld area, resulting in clean and high-quality welds.
Application: aerospace, automotive, petrochemical, and pipe fabrication, where high-quality welds and precise control over the welding process are essential.
2. Arc Welding
In arc welding, a high-voltage electric current is generated using the electrode, creating an arc between the electrode and the metal pieces. The electric arc produces intense heat, which melts the metals. And, welds it appropriately and after solidification it leaves perfect welds.

Application: Overall, arc welding is a widely used and effective welding technique that allows for strong and durable metal joins in a variety of applications, from large-scale industrial welding to small-scale repairs and fabrication.
3. Gas Metal Arc Welding/ MIG
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), also abbreviated as Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding. It is a welding process that uses a continuous and consumable wire electrode to join metals. It is a popular welding method due to its versatility and ease of use.

In MIG welding, a power source generates an electrical current that passes through the wire electrode, creating an electric arc between the electrode and the workpiece. This arc heats the metals, causing them to melt and fuse together. The wire electrode also acts as a filler material, adding molten metal to the weld joint.
The name “Metal Inert Gas” refers to the shielding gas used in the process. A flow of inert gas, such as argon or a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, is directed over the weld pool to protect it from atmospheric contamination. The shielding gas prevents oxidation and other impurities from affecting the quality of the weld.
Application: MIG welding is commonly used in various industries and applications, including automotive, construction, manufacturing, and general fabrication. It is suitable for welding a wide range of metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys.
4. Resistance Welding
Continuing to the laser welding techniques, the resistance welding technique is also a famous one. It includes aluminum surface adjoining by applying pressure techniques via electric currents. As, the heat produced melts the metal, and once it solidifies perfect welding over the materials.
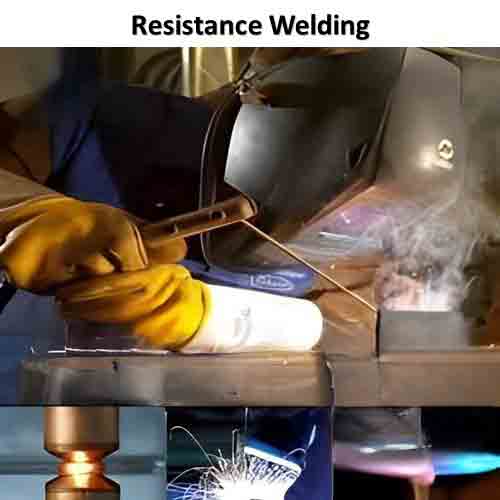

Applications: It is commonly used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, appliance production, construction, and aerospace.
5. Electron Beam Welding and Laser Beam Welding
Electron Beam Welding (EBW) and Laser Beam Welding (LBW) are both advanced welding processes that utilize focused beams of energy to join metal parts. While they are distinct processes, they share similarities in terms of their precision and applications.

It can create highly precise and narrow welds due to the focused electron beam. However, EBW requires a vacuum environment to prevent electron scattering and to maintain beam stability. This requirement limits its practicality for certain applications and materials.
Applications: aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical device manufacturing, and other industries where fine and accurate welding is required.
Easier method of welding aluminum
Electron Beam Welding (EBW):
You can go through the most demanding technique of aluminum welding via the EBW welding process. It utilizes a focused beam of high-velocity electrons to melt and join metals. In this process, electrons are accelerated to high speeds using an electron gun and directed toward the metal pieces.
Advantages
- It is an easy and clean process of welding over metallic surfaces.
- Using the high-tech machine welding software the welding operations are quite precise and time-efficient.
- It helps in asymmetrical material joining with welding perfections.
- You will not have to use filler material.
Summary
At last, we have concluded here the aluminum welding’s famous techniques perfectly. In addition, what is the perfect way of welding over the highly reflective metal category of aluminum. And what are the precautions we can use like wearing the protective attires and accessories to avoid any unpredicted accidents during the industrial aluminum welding operations. For knowing more Call or WhatsApp: 9804718718